As a programmer we develop a java application and when we compile a java program, the compiler will generate .class (dot class) file.The .class file contains byte code (Special java instructions).To execute a java program we take the help of JVM (java virtual machine) to the JVM we have to provide .class file as the input.
- As a programmer we develop a java application and when we compile a java program, the compiler will generate .class (dot class) file.
- The .class file contains byte code (Special java instructions).
- To execute a java program we take the help of JVM (java virtual machine) to the JVM we have to provide .class file as the input.
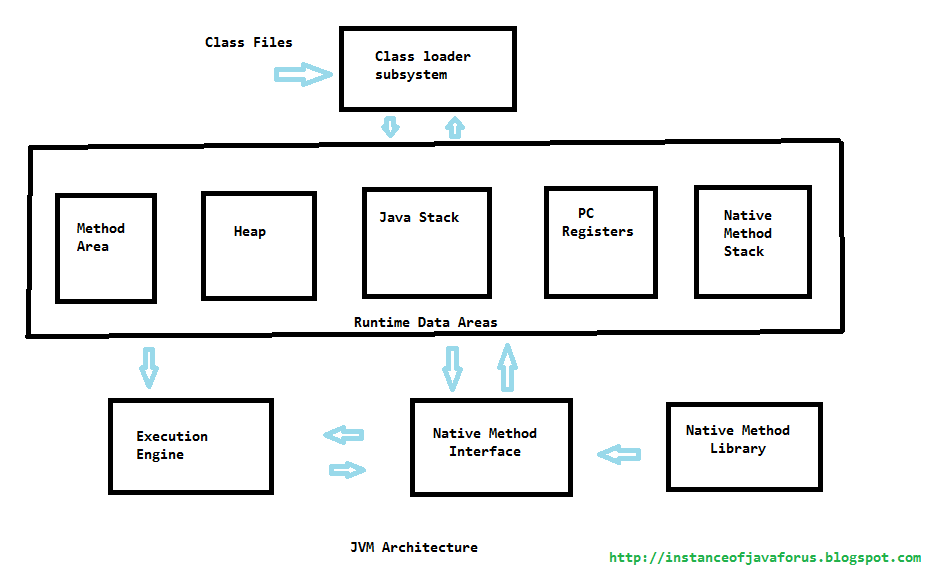
Class Loader Sub System:
- The class loader sub system will take a .class file as the input and performance the following operations.
- The class loader sub system is responsible for loading the .class file (Byte code) into the JVM.
- Before loading the Byte code into the JVM it will verify where there the Byte code is valid or not. This verification will be done by Byte code verifier.
- If the Byte code is valid then the memory for the Byte code will be allocated in different areas.
- The different areas into which the Byte code is loaded are called as Run Time Data Areas. The various run time data areas are.
1) Method Area: This Area can be used for storing all the class code and method code.
2) Heap Memory: This Area can be used for storing all the objects that are created.
3) Java Stack: This Area can be used for storing the information of the methods. That is under execution. The java stack can be considered as the combination of stack frames where every frame will contain the stat of a single method.
4) PC Register (program counter): This Register will contain address of the next instruction that have to be executed.
5) Java Native Stack: This area is used for storing non-java coding available in the application. The non-java code is called as native code.
Execution Engine:
The Execution Engine is Responsible for executing the program and it contains two parts.
- Interpreter
- JIT Compiler (just in time compiler)
Native Library:
- All the predefined programs required for executing the non-java code put to gather is called as Native Library.
Native Interface:
- The Native Interface is responsible for loading the programs form the Native Library to the: JVM.
- To execute a java program the JVM requires some resources from the machine to get those resources the JVM has to communicate with the operating system (OS). That is available in the underline machine.